Simple Linear Regression
Learning Outcomes
Linear Regression
Ordinary Least Squares
R Code
R Packages
Linear Regression
Linear Regression
Linear regression is used to model the association between a set of predictor variables (x’s) and an outcome variable (y). Linear regression will fit a line that best describes the data points.
Simple Linear Regression
Simple linear regression will model the association between one predictor variable and an outcome:
\[ Y = \beta_0 + \beta_1 X + \epsilon \]
\(\beta_0\): Intercept term
\(\beta_1\): Slope term
\(\epsilon\sim N(0,\sigma^2)\)
palmerpenguins
The palmerpenguins data set contains 344 observations of 7 penguin characteristics. We will be looking at different association of the penguins
Scatter Plot
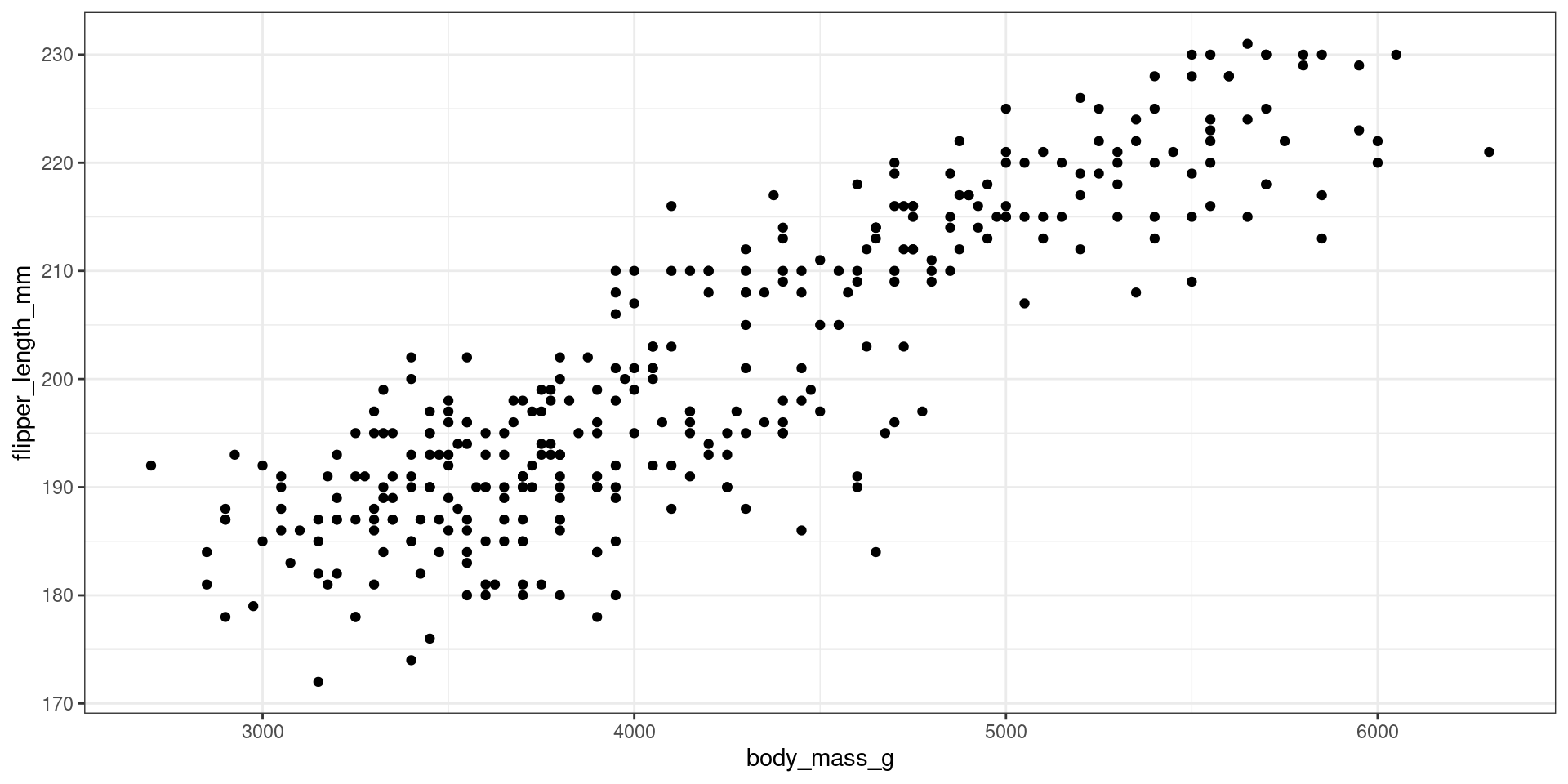
Scatter Plot
Fitting a Line
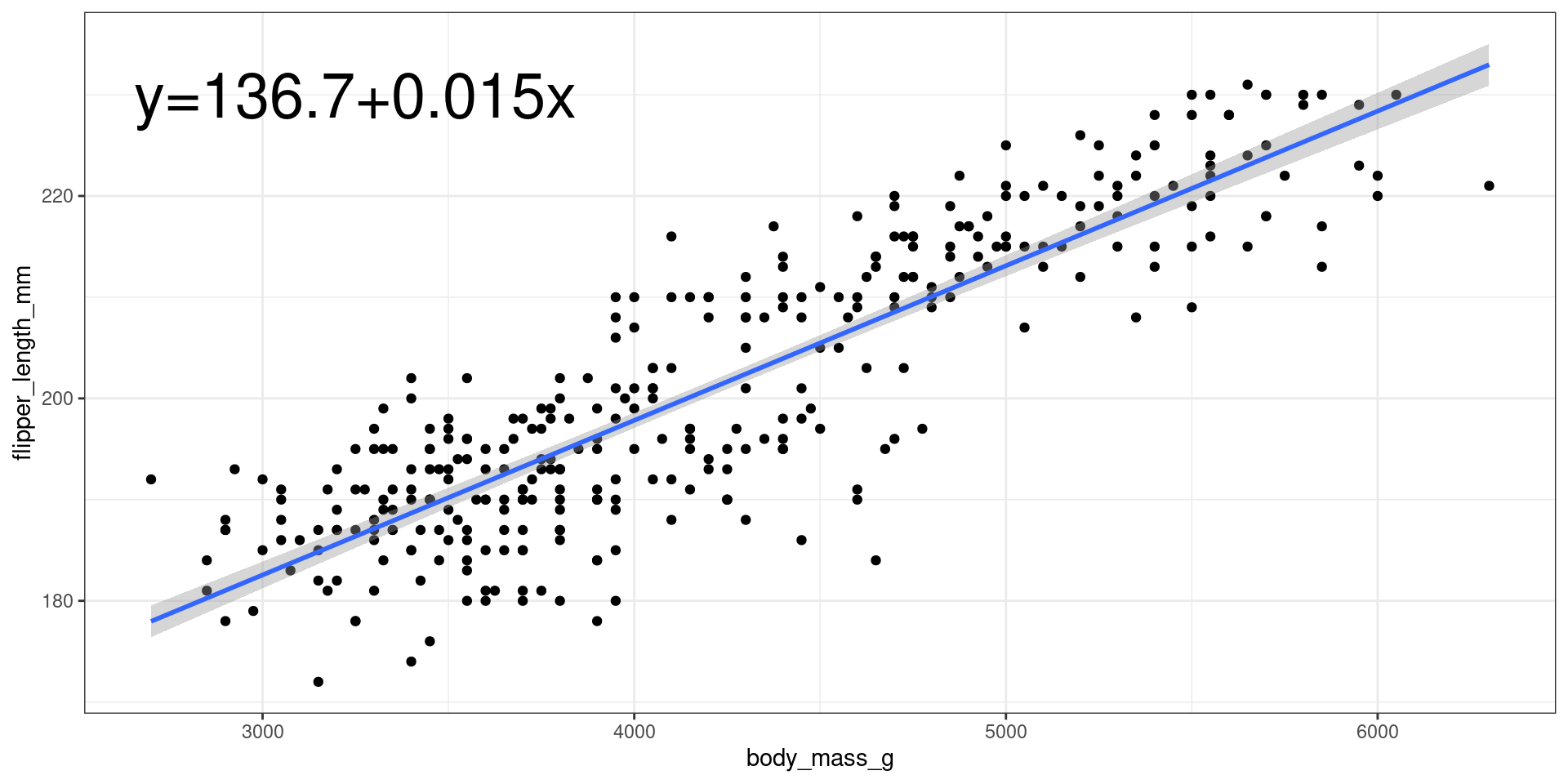
Interpretation
\[ \hat y = 136.73 + 0.015 x \]
Ordinary Least Squares
Ordinary Least Squares
For a data pair \((X_i,Y_i)_{i=1}^n\), the ordinary least squares estimator will find the estimates of \(\hat\beta_0\) and \(\hat\beta_1\) that minimize the following function:
\[ \sum^n_{i=1}\{y_i-(\beta_0+\beta_1x_i)\}^2 \]
Estimates
\[ \hat\beta_0 = \bar y - \hat\beta_1\bar x \] \[ \hat\beta_1 = \frac{\sum^n_{i=1}(y_i-\bar y)(x_i-\bar x)}{\sum^n_{i=1}(x_i-\bar x)^2} \] \[ \hat\sigma^2 = \frac{1}{n-2}\sum^n_{i=1}(y_i-\hat y_i)^2 \]
Standard Errors of \(\beta\)’s
Standard Errors of \(\beta\)’s
\[ SE(\hat\beta_0)=\sqrt{\frac{\sum^n_{i=1}x_i^2\hat\sigma^2}{n\sum^n_{i=1}(x_i-\bar x)^2}} \]
\[ SE(\hat\beta_1)=\sqrt\frac{\hat\sigma^2}{\sum^n_{i=1}(x_i-\bar x)^2} \]
Standard Error of \(\beta_0\)
Unbiasedness of \(\beta\)’s
Unbiasedness of \(\beta\)’s
Both \(\beta_0\) and \(\beta_1\) are unbiased estimators.
\(E(\beta_1)\)
Application in R
R Code
Use the lm() and summary() functions to fit a model and obtain the relevant statistics.
Fitting a line
Call:
lm(formula = bill_depth_mm ~ bill_length_mm, data = penguins)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-4.1381 -1.4263 0.0164 1.3841 4.5255
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 20.88547 0.84388 24.749 < 2e-16 ***
bill_length_mm -0.08502 0.01907 -4.459 1.12e-05 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 1.922 on 340 degrees of freedom
(2 observations deleted due to missingness)
Multiple R-squared: 0.05525, Adjusted R-squared: 0.05247
F-statistic: 19.88 on 1 and 340 DF, p-value: 1.12e-05